Masks Utils¶
supervision.detection.utils.masks.move_masks(masks: npt.NDArray[np.bool_], offset: npt.NDArray[np.int32], resolution_wh: tuple[int, int]) -> npt.NDArray[np.bool_]
¶
Offset the masks in an array by the specified (x, y) amount.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
|
NDArray[bool_]
|
A 3D array of binary masks corresponding to the
predictions. Shape: |
required |
|
NDArray[int32]
|
An array of shape |
required |
|
Tuple[int, int]
|
The width and height of the desired mask resolution. |
required |
Returns:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
NDArray[bool_]
|
(npt.NDArray[np.bool_]) repositioned masks, optionally padded to the specified shape. |
Examples:
>>> import numpy as np
>>> import supervision as sv
>>> mask = np.array([[[False, False, False, False],
... [False, True, True, False],
... [False, True, True, False],
... [False, False, False, False]]], dtype=bool)
>>> offset = np.array([1, 1])
>>> sv.move_masks(mask, offset, resolution_wh=(4, 4))
array([[[False, False, False, False],
[False, False, False, False],
[False, False, True, True],
[False, False, True, True]]])
>>> offset = np.array([-2, 2])
>>> sv.move_masks(mask, offset, resolution_wh=(4, 4))
array([[[False, False, False, False],
[False, False, False, False],
[False, False, False, False],
[ True, False, False, False]]])
Source code in src/supervision/detection/utils/masks.py
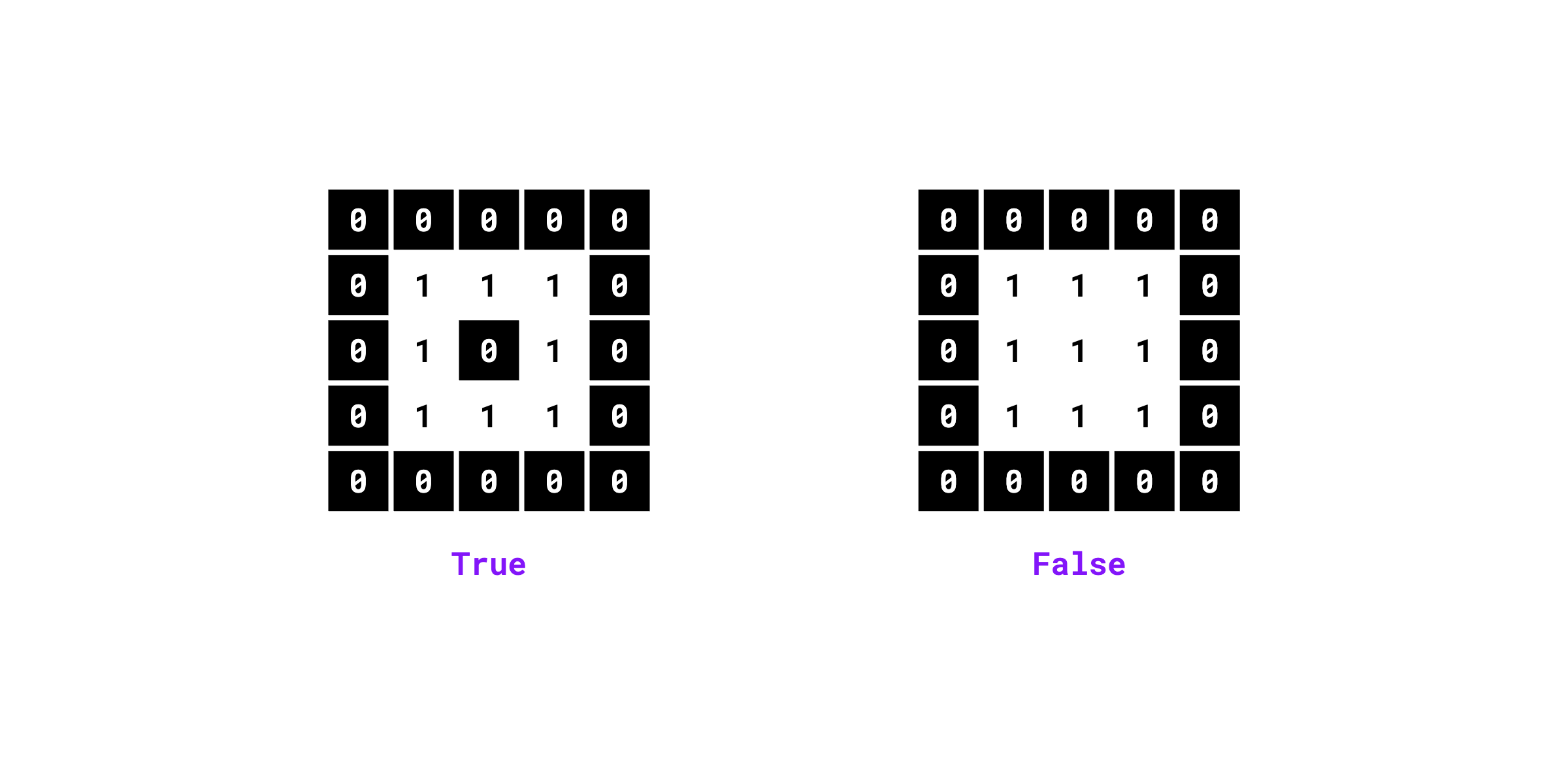
supervision.detection.utils.masks.contains_holes(mask: npt.NDArray[np.bool_]) -> bool
¶
Checks if the binary mask contains holes (background pixels fully enclosed by foreground pixels).
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
|
NDArray[bool_]
|
2D binary mask where |
required |
Returns:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
bool
|
True if holes are detected, False otherwise. |
Examples:
>>> import numpy as np
>>> import supervision as sv
>>> mask = np.array([
... [0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
... [0, 1, 1, 1, 0],
... [0, 1, 0, 1, 0],
... [0, 1, 1, 1, 0],
... [0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
... ]).astype(bool)
>>> sv.contains_holes(mask=mask)
True
>>> mask = np.array([
... [0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
... [0, 1, 1, 1, 0],
... [0, 1, 1, 1, 0],
... [0, 1, 1, 1, 0],
... [0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
... ]).astype(bool)
>>> sv.contains_holes(mask=mask)
False
Source code in src/supervision/detection/utils/masks.py
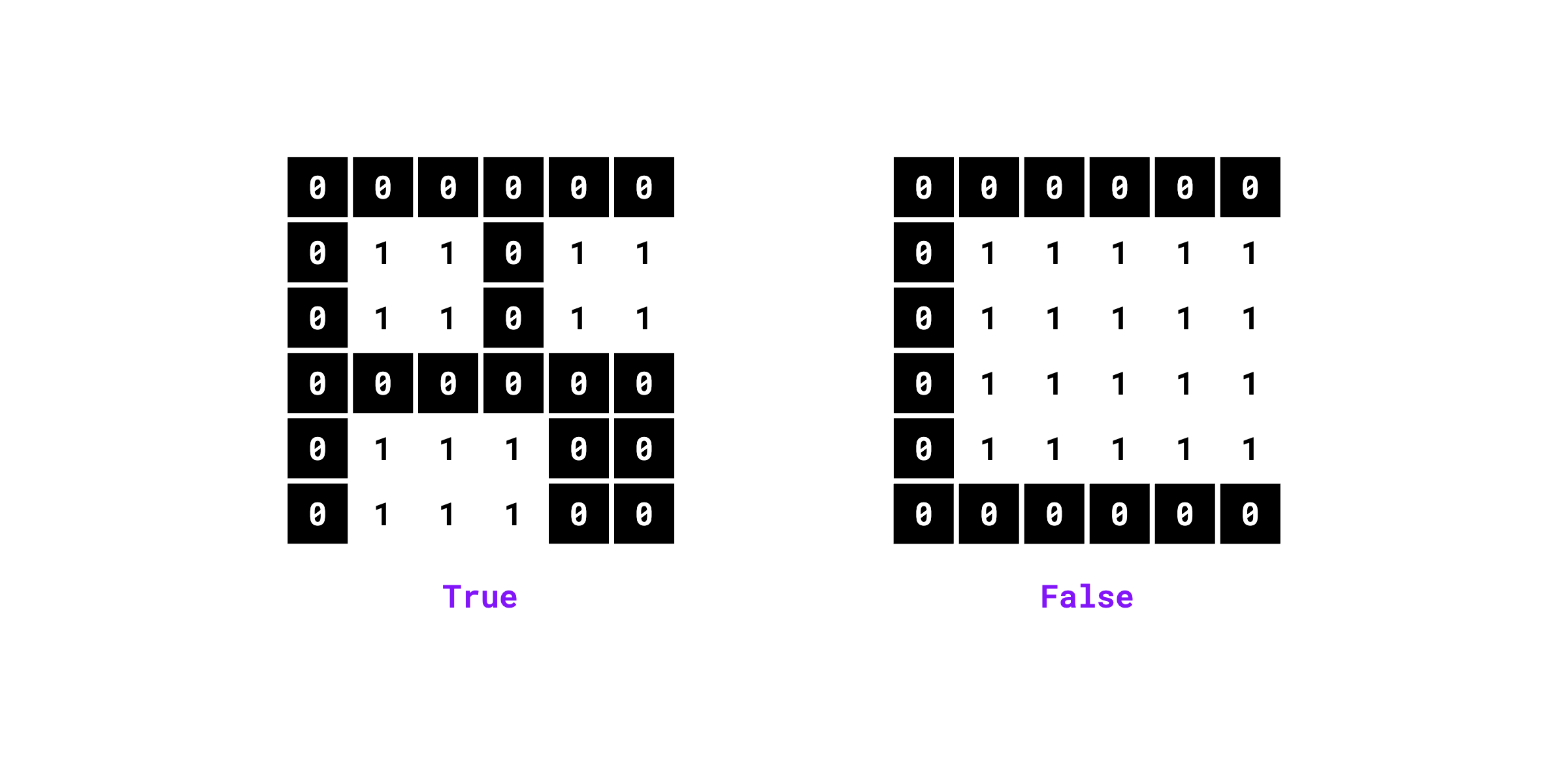
supervision.detection.utils.masks.contains_multiple_segments(mask: npt.NDArray[np.bool_], connectivity: int = 4) -> bool
¶
Checks if the binary mask contains multiple unconnected foreground segments.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
|
NDArray[bool_]
|
2D binary mask where |
required |
|
int)
|
Default: 4 is 4-way connectivity, which means that foreground pixels are the part of the same segment/component if their edges touch. Alternatively: 8 for 8-way connectivity, when foreground pixels are connected by their edges or corners touch. |
4
|
Returns:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
bool
|
True when the mask contains multiple not connected components, False otherwise. |
Raises:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
ValueError
|
If connectivity(int) parameter value is not 4 or 8. |
Examples:
>>> import numpy as np
>>> import supervision as sv
>>> mask = np.array([
... [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
... [0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1],
... [0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1],
... [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
... [0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0],
... [0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0]
... ]).astype(bool)
>>> sv.contains_multiple_segments(mask=mask, connectivity=4)
True
>>> mask = np.array([
... [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
... [0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
... [0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
... [0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
... [0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
... [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
... ]).astype(bool)
>>> sv.contains_multiple_segments(mask=mask, connectivity=4)
False
Source code in src/supervision/detection/utils/masks.py
supervision.detection.utils.masks.filter_segments_by_distance(mask: npt.NDArray[np.bool_], absolute_distance: float | None = 100.0, relative_distance: float | None = None, connectivity: int = 8, mode: Literal['edge', 'centroid'] = 'edge') -> npt.NDArray[np.bool_]
¶
Keep the largest connected component and any other components within a distance threshold.
Distance can be absolute in pixels or relative to the image diagonal.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
|
NDArray[bool_]
|
Boolean mask HxW. |
required |
|
float | None
|
Max allowed distance in pixels to the main component.
Ignored if |
100.0
|
|
float | None
|
Fraction of the diagonal. If set, threshold = fraction * sqrt(H^2 + W^2). |
None
|
|
int
|
8
|
|
|
Literal['edge', 'centroid']
|
Defines how distance between components is measured. - "edge": Uses distance between nearest edges (via distance transform). - "centroid": Uses distance between component centroids. |
'edge'
|
Returns:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
NDArray[bool_]
|
Boolean mask after filtering. |
Examples:
>>> import numpy as np
>>> import supervision as sv
>>> mask = np.array([
... [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
... [0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
... [0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
... [0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0],
... [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0],
... [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
... [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
... [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
... [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0],
... [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0],
... [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
... [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
... ], dtype=bool)
>>> sv.filter_segments_by_distance(
... mask,
... absolute_distance=3,
... mode="edge",
... connectivity=8
... ).astype(int)
array([[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]])
The nearby 2×2 block at columns 6–7 is kept because its edge distance is within 3 pixels. The distant block at columns 9-10 is removed.
Source code in src/supervision/detection/utils/masks.py
265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 330 331 332 333 334 335 336 337 338 339 340 341 342 343 344 345 346 347 348 349 350 351 352 353 354 355 356 357 358 359 360 361 362 363 364 365 366 367 368 369 370 371 372 373 374 375 376 377 378 379 380 381 382 383 384 385 386 387 388 389 390 391 392 393 394 395 396 | |