Detection Utils¶
Compute Intersection over Union (IoU) of two sets of bounding boxes -
boxes_true and boxes_detection. Both sets
of boxes are expected to be in (x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max) format.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
|
ndarray
|
2D |
required |
|
ndarray
|
2D |
required |
Returns:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
ndarray
|
np.ndarray: Pairwise IoU of boxes from |
Source code in supervision/detection/utils.py
Compute Intersection over Union (IoU) of two sets of masks -
masks_true and masks_detection.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
|
ndarray
|
3D |
required |
|
ndarray
|
3D |
required |
|
int
|
memory limit in MB, default is 1024 * 5 MB (5GB). |
1024 * 5
|
Returns:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
ndarray
|
np.ndarray: Pairwise IoU of masks from |
Source code in supervision/detection/utils.py
Compute Intersection over Union (IoU) of two sets of oriented bounding boxes -
boxes_true and boxes_detection. Both sets of boxes are expected to be in
((x1, y1), (x2, y2), (x3, y3), (x4, y4)) format.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
|
ndarray
|
a |
required |
|
ndarray
|
a |
required |
Returns:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
ndarray
|
np.ndarray: Pairwise IoU of boxes from |
Source code in supervision/detection/utils.py
Generate a mask from a polygon.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
|
ndarray
|
The polygon for which the mask should be generated, given as a list of vertices. |
required |
|
Tuple[int, int]
|
The width and height of the desired resolution. |
required |
Returns:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
ndarray
|
np.ndarray: The generated 2D mask, where the polygon is marked with
|
Source code in supervision/detection/utils.py
Converts a 3D np.array of 2D bool masks into a 2D np.array of bounding boxes.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
|
ndarray
|
A 3D |
required |
Returns:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
ndarray
|
np.ndarray: A 2D |
Source code in supervision/detection/utils.py
Converts a binary mask to a list of polygons.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
|
ndarray
|
A binary mask represented as a 2D NumPy array of
shape |
required |
Returns:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
List[ndarray]
|
List[np.ndarray]: A list of polygons, where each polygon is represented by a
NumPy array of shape |
Source code in supervision/detection/utils.py
Converts a polygon represented by a NumPy array into a bounding box.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
|
ndarray
|
A polygon represented by a NumPy array of shape |
required |
Returns:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
ndarray
|
np.ndarray: A 1D NumPy array containing the bounding box
|
Source code in supervision/detection/utils.py
Filters a list of polygons based on their area.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
|
List[ndarray]
|
A list of polygons, where each polygon is
represented by a NumPy array of shape |
required |
|
Optional[float]
|
The minimum area threshold. Only polygons with an area greater than or equal to this value will be included in the output. If set to None, no minimum area constraint will be applied. |
None
|
|
Optional[float]
|
The maximum area threshold. Only polygons with an area less than or equal to this value will be included in the output. If set to None, no maximum area constraint will be applied. |
None
|
Returns:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
List[ndarray]
|
List[np.ndarray]: A new list of polygons containing only those with areas within the specified thresholds. |
Source code in supervision/detection/utils.py
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
|
NDArray[float64]
|
An array of shape |
required |
|
array
|
An array of shape |
required |
Returns:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
NDArray[float64]
|
npt.NDArray[np.float64]: Repositioned bounding boxes. |
Examples:
import numpy as np
import supervision as sv
xyxy = np.array([
[10, 10, 20, 20],
[30, 30, 40, 40]
])
offset = np.array([5, 5])
sv.move_boxes(xyxy=xyxy, offset=offset)
# array([
# [15, 15, 25, 25],
# [35, 35, 45, 45]
# ])
Source code in supervision/detection/utils.py
Offset the masks in an array by the specified (x, y) amount.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
|
NDArray[bool_]
|
A 3D array of binary masks corresponding to the
predictions. Shape: |
required |
|
NDArray[int32]
|
An array of shape |
required |
|
Tuple[int, int]
|
The width and height of the desired mask resolution. |
required |
Returns:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
NDArray[bool_]
|
(npt.NDArray[np.bool_]) repositioned masks, optionally padded to the specified shape. |
Examples:
import numpy as np
import supervision as sv
mask = np.array([[[False, False, False, False],
[False, True, True, False],
[False, True, True, False],
[False, False, False, False]]], dtype=bool)
offset = np.array([1, 1])
sv.move_masks(mask, offset, resolution_wh=(4, 4))
# array([[[False, False, False, False],
# [False, False, False, False],
# [False, False, True, True],
# [False, False, True, True]]], dtype=bool)
offset = np.array([-2, 2])
sv.move_masks(mask, offset, resolution_wh=(4, 4))
# array([[[False, False, False, False],
# [False, False, False, False],
# [False, False, False, False],
# [True, False, False, False]]], dtype=bool)
Source code in supervision/detection/utils.py
748 749 750 751 752 753 754 755 756 757 758 759 760 761 762 763 764 765 766 767 768 769 770 771 772 773 774 775 776 777 778 779 780 781 782 783 784 785 786 787 788 789 790 791 792 793 794 795 796 797 798 799 800 801 802 803 804 805 806 807 808 809 810 811 812 813 814 815 816 817 818 819 820 821 822 823 824 825 826 | |
Scale the dimensions of bounding boxes.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
|
NDArray[float64]
|
An array of shape |
required |
|
float
|
A float value representing the factor by which the box dimensions are scaled. A factor greater than 1 enlarges the boxes, while a factor less than 1 shrinks them. |
required |
Returns:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
NDArray[float64]
|
npt.NDArray[np.float64]: Scaled bounding boxes. |
Examples:
import numpy as np
import supervision as sv
xyxy = np.array([
[10, 10, 20, 20],
[30, 30, 40, 40]
])
sv.scale_boxes(xyxy=xyxy, factor=1.5)
# array([
# [ 7.5, 7.5, 22.5, 22.5],
# [27.5, 27.5, 42.5, 42.5]
# ])
Source code in supervision/detection/utils.py
Clips bounding boxes coordinates to fit within the frame resolution.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
|
ndarray
|
A numpy array of shape |
required |
|
Tuple[int, int]
|
A tuple of the form |
required |
Returns:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
ndarray
|
np.ndarray: A numpy array of shape |
Examples:
import numpy as np
import supervision as sv
xyxy = np.array([
[10, 20, 300, 200],
[15, 25, 350, 450],
[-10, -20, 30, 40]
])
sv.clip_boxes(xyxy=xyxy, resolution_wh=(320, 240))
# array([
# [ 10, 20, 300, 200],
# [ 15, 25, 320, 240],
# [ 0, 0, 30, 40]
# ])
Source code in supervision/detection/utils.py
Pads bounding boxes coordinates with a constant padding.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
|
ndarray
|
A numpy array of shape |
required |
|
int
|
The padding value to be added to both the left and right sides of each bounding box. |
required |
|
Optional[int]
|
The padding value to be added to both the top and bottom
sides of each bounding box. If not provided, |
None
|
Returns:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
ndarray
|
np.ndarray: A numpy array of shape |
Examples:
import numpy as np
import supervision as sv
xyxy = np.array([
[10, 20, 30, 40],
[15, 25, 35, 45]
])
sv.pad_boxes(xyxy=xyxy, px=5, py=10)
# array([
# [ 5, 10, 35, 50],
# [10, 15, 40, 55]
# ])
Source code in supervision/detection/utils.py
Converts bounding box coordinates from (x, y, width, height)
format to (x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max) format.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
|
ndarray
|
A numpy array of shape |
required |
Returns:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
ndarray
|
np.ndarray: A numpy array of shape |
Examples:
import numpy as np
import supervision as sv
xywh = np.array([
[10, 20, 30, 40],
[15, 25, 35, 45]
])
sv.xywh_to_xyxy(xywh=xywh)
# array([
# [10, 20, 40, 60],
# [15, 25, 50, 70]
# ])
Source code in supervision/detection/utils.py
Converts bounding box coordinates from (x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max)
format to (x, y, width, height) format.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
|
ndarray
|
A numpy array of shape |
required |
Returns:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
ndarray
|
np.ndarray: A numpy array of shape |
Examples:
import numpy as np
import supervision as sv
xyxy = np.array([
[10, 20, 40, 60],
[15, 25, 50, 70]
])
sv.xyxy_to_xywh(xyxy=xyxy)
# array([
# [10, 20, 30, 40],
# [15, 25, 35, 45]
# ])
Source code in supervision/detection/utils.py
Converts bounding box coordinates from (center_x, center_y, width, height)
format to (x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max) format.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
|
ndarray
|
A numpy array of shape |
required |
Returns:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
ndarray
|
np.ndarray: A numpy array of shape |
Examples:
import numpy as np
import supervision as sv
xcycwh = np.array([
[50, 50, 20, 30],
[30, 40, 10, 15]
])
sv.xcycwh_to_xyxy(xcycwh=xcycwh)
# array([
# [40, 35, 60, 65],
# [25, 32.5, 35, 47.5]
# ])
Source code in supervision/detection/utils.py
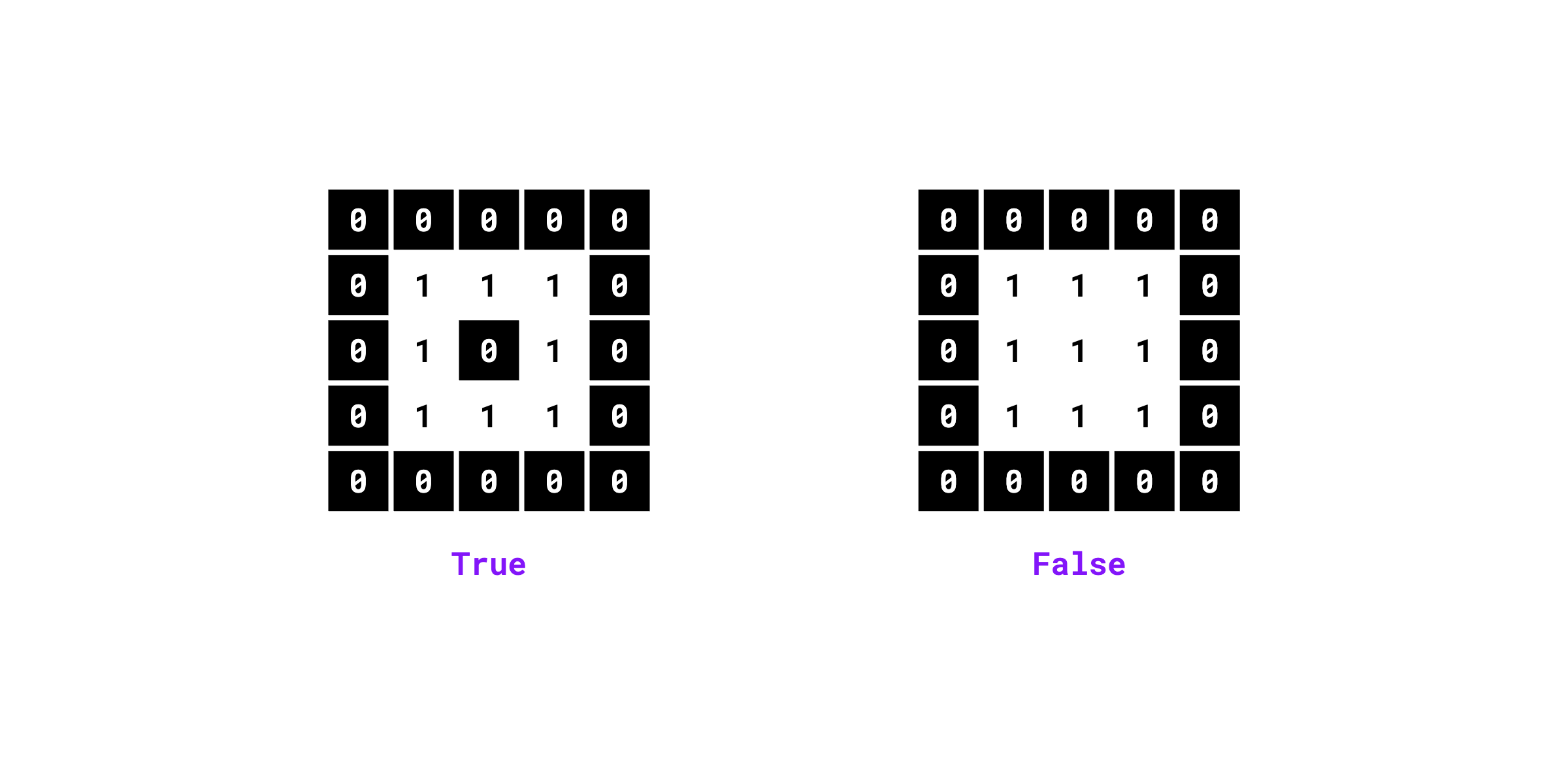
Checks if the binary mask contains holes (background pixels fully enclosed by foreground pixels).
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
|
NDArray[bool_]
|
2D binary mask where |
required |
Returns:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
bool
|
True if holes are detected, False otherwise. |
Examples:
import numpy as np
import supervision as sv
mask = np.array([
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
]).astype(bool)
sv.contains_holes(mask=mask)
# True
mask = np.array([
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
]).astype(bool)
sv.contains_holes(mask=mask)
# False
Source code in supervision/detection/utils.py
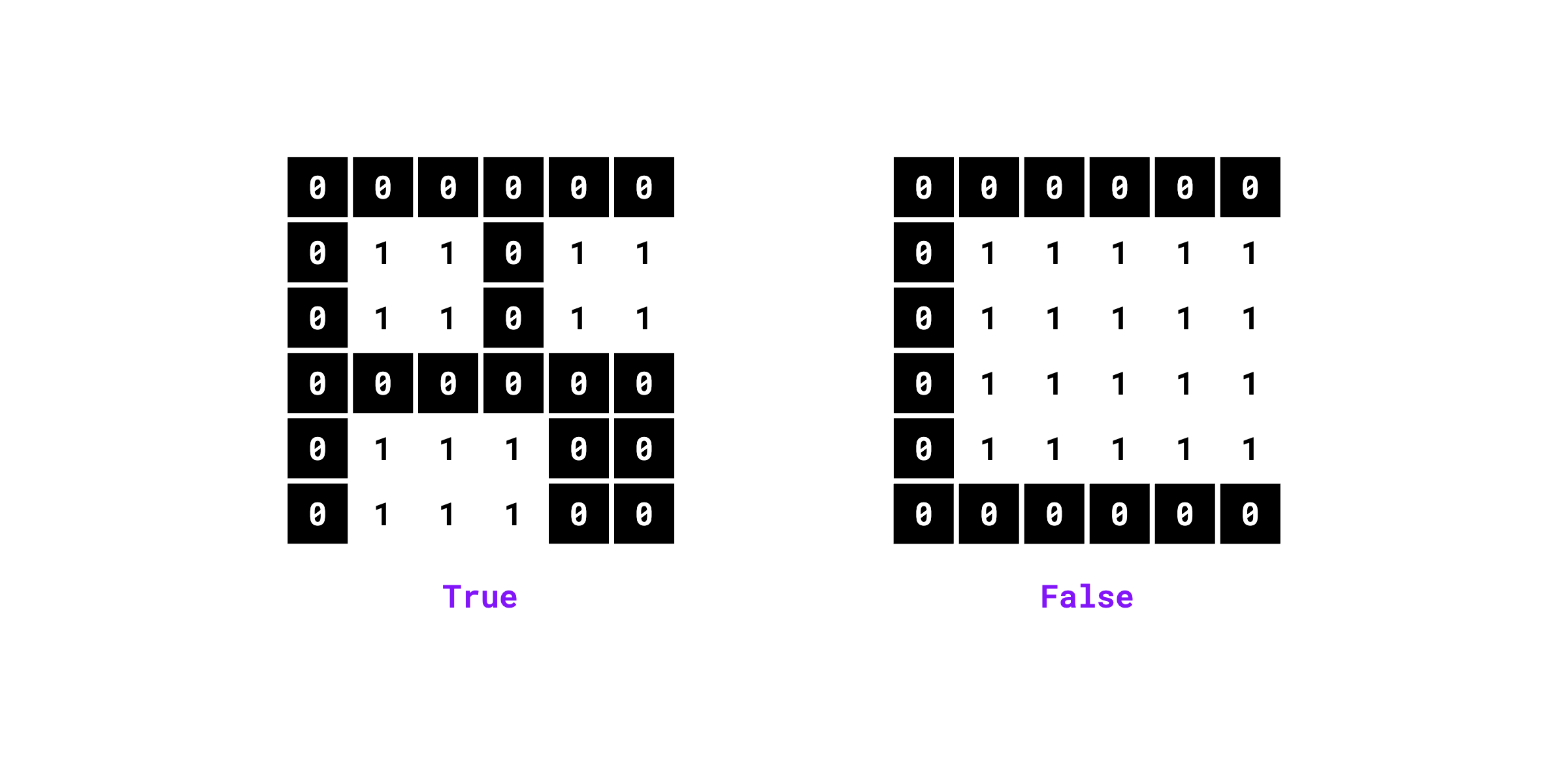
Checks if the binary mask contains multiple unconnected foreground segments.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
|
NDArray[bool_]
|
2D binary mask where |
required |
|
int)
|
Default: 4 is 4-way connectivity, which means that foreground pixels are the part of the same segment/component if their edges touch. Alternatively: 8 for 8-way connectivity, when foreground pixels are connected by their edges or corners touch. |
4
|
Returns:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
bool
|
True when the mask contains multiple not connected components, False otherwise. |
Raises:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
ValueError
|
If connectivity(int) parameter value is not 4 or 8. |
Examples:
import numpy as np
import supervision as sv
mask = np.array([
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1],
[0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0]
]).astype(bool)
sv.contains_multiple_segments(mask=mask, connectivity=4)
# True
mask = np.array([
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
]).astype(bool)
sv.contains_multiple_segments(mask=mask, connectivity=4)
# False
Source code in supervision/detection/utils.py
1142 1143 1144 1145 1146 1147 1148 1149 1150 1151 1152 1153 1154 1155 1156 1157 1158 1159 1160 1161 1162 1163 1164 1165 1166 1167 1168 1169 1170 1171 1172 1173 1174 1175 1176 1177 1178 1179 1180 1181 1182 1183 1184 1185 1186 1187 1188 1189 1190 1191 1192 1193 1194 1195 1196 1197 1198 1199 1200 1201 1202 1203 1204 | |